MRI OF FAT PAD IMPINGEMENT AROUND THE KNEE
Knee fat pad impingement syndromes are characterized by pain and inflammation of the fat pads surrounding the knee joint and can significantly impact knee function.
This blog post looks at the anatomy of the knee fat pads, the MRI appearance of impingement, and key areas to focus on MRI , to make accurate an diagnoses and guide appropriate treatment decisions.
There are four fat pads around the knee that can become impinged and can be symptomatic.

Quadriceps fat pad:
Located above the patella and posterior to the quadriceps tendon.Supratrochlear fat pad:
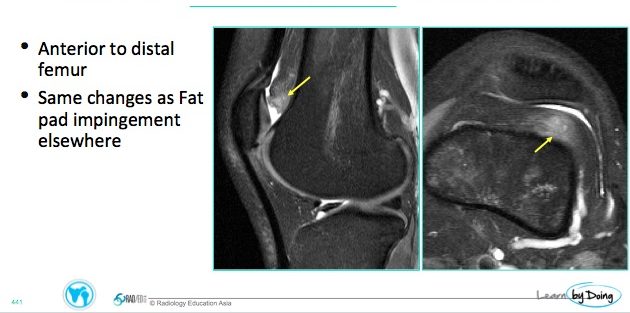
Situated anterior to the femoral trochlea.Hoffa's fat pad:
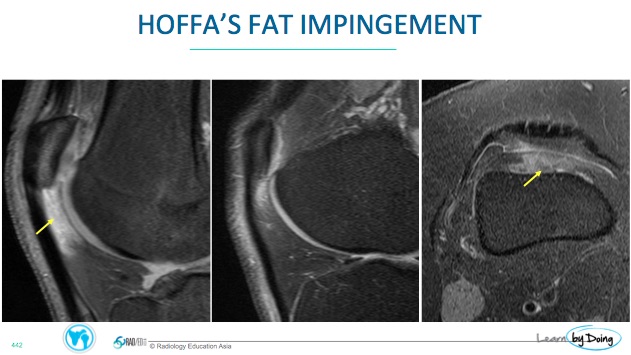
Positioned behind the patella/ patella tendon and tibia.
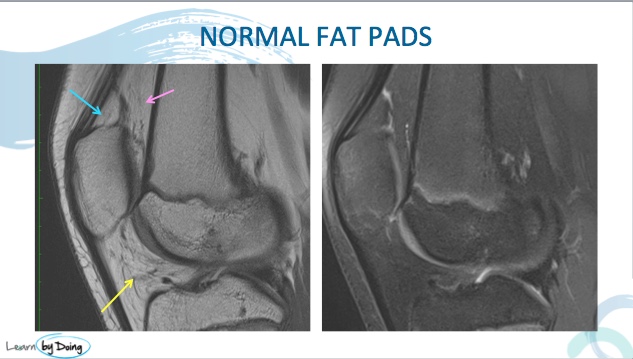
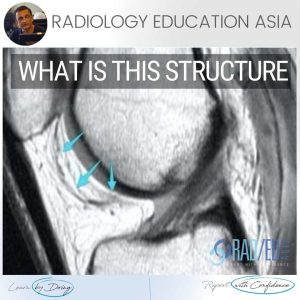
Image Above: Location for quadriceps fat pad (Blue Arrow), Supratrochlear Fat Pad (Pink arrow) and Hoffa's Fat Pad (yellow arrow).
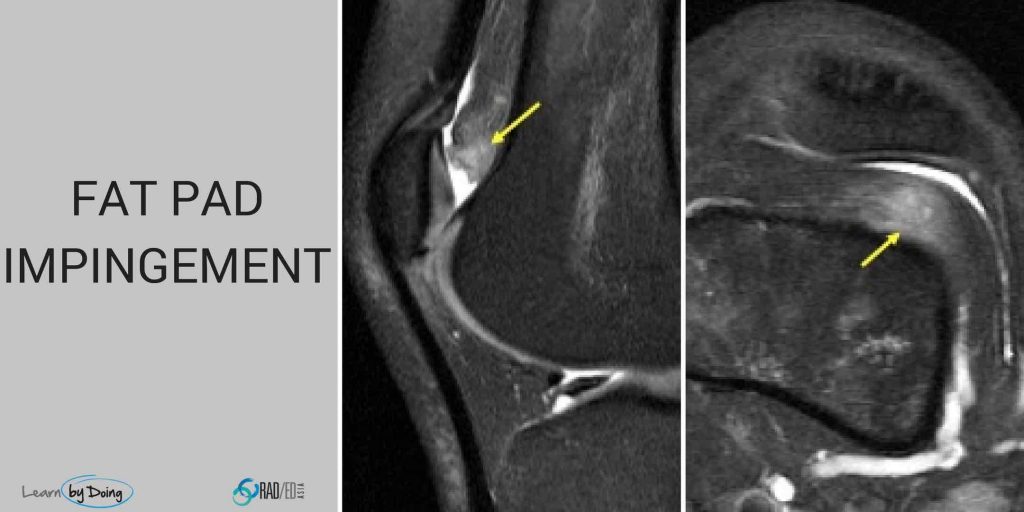
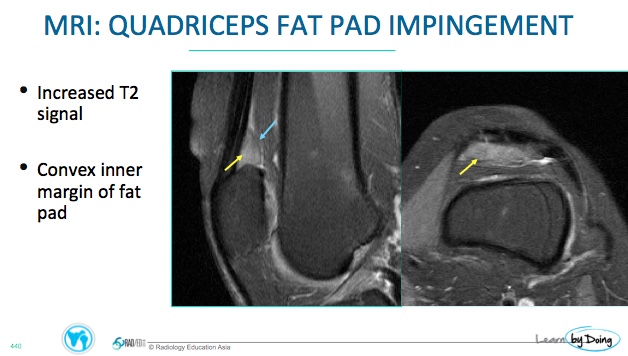
On MRI Impingement of any of the fat pads has a similar appearance and the best sequence to diagnose it is on a STIR/T2FS or PDFS sequence.
Look for
Increased signal intensity on fluid-sensitive sequences (PDFS, STIR, T2-weighted) in the affected fat pad.
Low signal intensity on T1-weighted images.
Edema may extend to surrounding soft tissues.
- Expansion of the contours of the fat pad which become convex. This is usually seen in the Quadriceps and Supratrochlear fat pads and not in Hoffa's fat pad.
- C+: There is no need to give contrast but if you do, impingement in the acute and subacute stages will enhance.

For all our other current MSK MRI & Spine MRI
Online Guided Mini Fellowships.
Click on the image below for more information.
- Join our WhatsApp Group for regular educational posts. Message “JOIN GROUP” to +6594882623 (your name and number remain private and cannot be seen by others).
- Get our weekly email with all our educational posts: https://bit.ly/whathappendthisweek
#radedasia #mri #mskmri #radiology